Abstract
Case Report
Methotrexate in management of Morbidly Adherent Placenta at Latifa Hospital, DHA, Dubai, UAE.: Case report
Atif BE Fazari*, Maria Eugenia Ramirez Aristondo, Faiqa Azim, Basma Abdo AlMaamari and Rasha Eltayeb
Published: 12 July, 2019 | Volume 2 - Issue 2 | Pages: 090-094
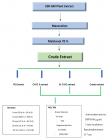
Morbidly adherent placenta (MAP) includes the spectrum of placenta accreta, increta, and percreta. It is a major cause of obstetric hemorrhage. Caesarean section is main risk factor for MAP. Ultrasound scan is highly sensitive method for MAP diagnosis and sometime Magnetic resonance image is of choice. Early diagnosis timed elective planned intervention after preparation under skillful multidisciplinary team improve the outcome and minimize the morbidity. Caesarean hysterectomy, major arteries ligation, arteries embolization and leave the placenta in-situ all are choices of management. Use of Methotrexate for the placenta in-situ in MAP is still debatable. We present a case of MAP in which placenta left in- situ followed by multiple Methotrexate injection during postpartum with good outcome and acceptability.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001027 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Morbidly adherent placenta; Placenta in-situ; Methotrexate
References
- Jauniaux ERM, Alfirevic Z, Bhide AG, Belfort MA, Burton GJ, et al. Placenta Praevia and Placenta Accreta: Diagnosis and Management. Green-top Guideline No. 27a. BJOG. 2019; 126: e1-e48. PubMed.: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30260097
- Babaei MR, Oveysi Kian M, Naderi Z, Khodaverdi S, Raoofi Z, et al., Methotrexate infusion followed by uterine artery embolisation for the management of placental adhesive disorders: a case series. Clin Radiol. 2019; 74: 378-383. PubMed.: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30755315
- Khan M. Sachdeva R, Arora R, Bhasin S. Conservative management of morbidly adherant placenta–A case report and review of literature. Placenta. 2013; 34: 963-966. PubMed.: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23937959
- Arulkumaran S, Ng CS, Ingemarsson I, Ratnam SS. Medical treatment of placenta accreta with methotrexate. Acta Obstet Gynecologica Scand. 1986; 65: 285-286. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/3739639
- Matsuzaki S, Yoshino K, Endo M, Kakigano A, Takiuchi T, et al. Conservative management of placenta percreta. Int J Obstet Gynecol. 2017.
- Baker T, Datta P, Rewers-Felkins K, Thomas W. Breastfeeding Medicine. 2018.
- Timmermans S, van Hof AC, Duvekot JJ. Conservative management of abnormally invasive placentation. Obstet Gynecol Surv. 2007; 62: 529–539. PubMed.: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17634154
- Matsubara S, Takahashi H, Usui R. Letter to ‘Retrospective analysis: Conservative treatment of placenta increta with methotrexate’: Some clarifications. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2018; 44: 1499-1500. PubMed.: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29932489
- MacGibbon A, Ius YM. Conservative Management of Abnormally Invasive Placenta Previa after Midtrimester Foetal Demise. Case Rep Obstet Gynecol. 2018; 7478437. PubMed.: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30405926
- Chaudhari HK, Shah PK, D'Souza N. Morbidly Adherent Placenta: Its Management and Maternal and Perinatal Outcome. J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2016; 67: 42-47. PubMed.: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28242967
- Ann S LaCasce. Therapeutic use and toxicity of high-dose methotrexate. 2018.
- Joel M Kremer. Major side effects of low-dose methotrexate. 2018
Figures:
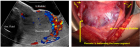
Figure 1
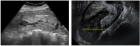
Figure 2
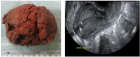
Figure 3
Similar Articles
-
The Case of the Phantom Trophoblastic TumorBenedict B Benigno*. The Case of the Phantom Trophoblastic Tumor. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001004; 1: 024-025
-
Methotrexate in management of Morbidly Adherent Placenta at Latifa Hospital, DHA, Dubai, UAE.: Case reportAtif BE Fazari*,Maria Eugenia Ramirez Aristondo,Faiqa Azim,Basma Abdo AlMaamari,Rasha Eltayeb. Methotrexate in management of Morbidly Adherent Placenta at Latifa Hospital, DHA, Dubai, UAE.: Case report. . 2019 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001027; 2: 090-094
-
Cervical choriocarcinoma in a post-menopause woman: Case report and review of literatureZeinab Nazari,Leila Mortazavi*,Noushin Gordani. Cervical choriocarcinoma in a post-menopause woman: Case report and review of literature. . 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001101; 5: 019-021
-
Cesarean scar pregnancy: A clinical case reportAziz Slaoui*,Aicha Bennani,Roughaya Tayeb,Najia Zeraidi,Amina Lakhdar,Aziz Baydada,Aicha Kharbach. Cesarean scar pregnancy: A clinical case report. . 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001119; 6: 006-009
-
Understanding and Managing Caesarean Scar Ectopic Pregnancy: A Retrospective Analysis of Risk Factors, Strategies, and OutcomesAbdullah Aldawsari*,Heba Al-hussaini*. Understanding and Managing Caesarean Scar Ectopic Pregnancy: A Retrospective Analysis of Risk Factors, Strategies, and Outcomes. . 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001176; 7: 115-116
Recently Viewed
-
Optimizing Treatment of Depression, Trauma, and Anxiety Disorders through Neurophysiological InterventionsKees Blasé*. Optimizing Treatment of Depression, Trauma, and Anxiety Disorders through Neurophysiological Interventions. Insights Depress Anxiety. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.ida.1001046; 9: 027-029
-
A Study on Incidence, Risk Factors, and Maternal Outcome of Placenta Accreta Spectrum in a Tertiary Care HospitalMittapalli Jyothirmayee**. A Study on Incidence, Risk Factors, and Maternal Outcome of Placenta Accreta Spectrum in a Tertiary Care Hospital. Clin J Obstet Gynecol. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001191; 8: 074-00
-
Breast Imaging Services Utilization Trends Across Private and Government-Insured Patients in a National Radiology PracticeAndrew K Hillman*,Phil Ramis,Patrick Nielsen,Sophia N Swanston,Dana Bonaminio,Eric M Rohren. Breast Imaging Services Utilization Trends Across Private and Government-Insured Patients in a National Radiology Practice. J Clin Med Exp Images. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcmei.1001037; 9: 020-027
-
A Rare Consanguineous Case of Alazami Syndrome in a Jordanian Family: Clinical Presentation, Genetic Analysis, and Therapeutic Approaches - A Case ReportFawzi Irshaid*, Salim Alawneh, Qasim Al Souhail, Aisha Alshdefat, Bashar Irshaid, Ahmed Irshaid. A Rare Consanguineous Case of Alazami Syndrome in a Jordanian Family: Clinical Presentation, Genetic Analysis, and Therapeutic Approaches - A Case Report. J Clin Med Exp Images. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcmei.1001031; 8: 003-006
-
Fiesta vs. Stress Condition the Incidence and the Age at Menarche. Forty Years of ResearchCarlos Y Valenzuela*. Fiesta vs. Stress Condition the Incidence and the Age at Menarche. Forty Years of Research. Clin J Obstet Gynecol. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001190; 8: 069-073
Most Viewed
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Evaluation of In vitro and Ex vivo Models for Studying the Effectiveness of Vaginal Drug Systems in Controlling Microbe Infections: A Systematic ReviewMohammad Hossein Karami*, Majid Abdouss*, Mandana Karami. Evaluation of In vitro and Ex vivo Models for Studying the Effectiveness of Vaginal Drug Systems in Controlling Microbe Infections: A Systematic Review. Clin J Obstet Gynecol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.cjog.1001151; 6: 201-215
-
Causal Link between Human Blood Metabolites and Asthma: An Investigation Using Mendelian RandomizationYong-Qing Zhu, Xiao-Yan Meng, Jing-Hua Yang*. Causal Link between Human Blood Metabolites and Asthma: An Investigation Using Mendelian Randomization. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001032; 7: 012-022
-
Impact of Latex Sensitization on Asthma and Rhinitis Progression: A Study at Abidjan-Cocody University Hospital - Côte d’Ivoire (Progression of Asthma and Rhinitis related to Latex Sensitization)Dasse Sery Romuald*, KL Siransy, N Koffi, RO Yeboah, EK Nguessan, HA Adou, VP Goran-Kouacou, AU Assi, JY Seri, S Moussa, D Oura, CL Memel, H Koya, E Atoukoula. Impact of Latex Sensitization on Asthma and Rhinitis Progression: A Study at Abidjan-Cocody University Hospital - Côte d’Ivoire (Progression of Asthma and Rhinitis related to Latex Sensitization). Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001035; 8: 007-012
-
An algorithm to safely manage oral food challenge in an office-based setting for children with multiple food allergiesNathalie Cottel,Aïcha Dieme,Véronique Orcel,Yannick Chantran,Mélisande Bourgoin-Heck,Jocelyne Just. An algorithm to safely manage oral food challenge in an office-based setting for children with multiple food allergies. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001027; 5: 030-037

If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."